Rapid Quantum Magnetic IL-6 Point-of-Care Assay in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19
Published in Diagnostics.
Authors
Johnny Atallah, Dakota Archambault, Jeffrey D Randall, Adam Shepro, Lauren E Styskal, David R Glenn, Colin B Connolly, Katelin Katsis, Kathleen Gallagher, Musie Ghebremichael, Michael K Mansour
Paper presented by Dr. Reinis Svarcbahs and selected by the NIDA TDI Paper of the Month Committee
Background and Technological Advancement
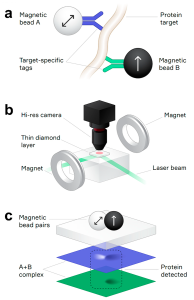
Detection of low levels of molecular targets (e.g. proteins) in biological samples is often limited by the signal-to-noise ratio. Additionally, long assay times are required for ultrasensitive detection methods that are not always practical for clinical use. Quantum diamond microscope system uses synthetic diamond chips with quantum defects also called nitrogen vacancy (NV) centers. NV centers can be considered pseudo atoms with electronic states that are sensitive to electric and magnetic fields and temperature and strain gradients. When NV centers are excited with green light, red fluorescence emitted from the NV centers detect local magnetic field. Fluorescence is measured over a millimeter-scale field of view providing millions of independent magnetic measurements to be made simultaneously. A target, for example IL-6, is detected by immunocomplexes that are bound to pairs of magnetically distinct beads that each have antibody recognizing different epitope of same antigen. When an external magnetic field is applied, the complexed beads are detected by NV centers. In practice, these spatially overlapped magnetic signals are considered a true signal while unbound beads appear as a non-coincident signal. This method does not require removal of unbound beads or extensive wash steps thus providing relatively fast and sensitive assay for measuring protein targets in pre-clinical and clinical applications. Overall, the quantum diamond microscope system is a sensitive method to detect target proteins in a short time compared to similar immunocomplex-based detection methods (e.g. traditional ELISAs). In theory, this method could be optimized for DNA and RNA targets.
Rapid Quantum Magnetic IL-6 Point-of-Care Assay in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 Journal Article
In: Diagnostics (Basel), vol. 12, no. 5, 2022, ISSN: 2075-4418.