Featured Paper of the Month – November 2016
Warren, Brandon L; Mendoza, Michael P; Cruz, Fabio C; Leao, Rodrigo M; Caprioli, Daniele; Rubio, Javier F; Whitaker, Leslie R; McPherson, Kylie B; Bossert, Jennifer M; Shaham, Yavin; Hope, Bruce T
Distinct Fos-Expressing Neuronal Ensembles in the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex Mediate Food Reward and Extinction Memories. Journal Article
In: J Neurosci, vol. 36, no. 25, pp. 6691–6703, 2016, ISSN: 1529-2401 (Electronic); 0270-6474 (Linking).
@article{Warren:2016aa,
title = {Distinct Fos-Expressing Neuronal Ensembles in the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex Mediate Food Reward and Extinction Memories.},
author = {Brandon L Warren and Michael P Mendoza and Fabio C Cruz and Rodrigo M Leao and Daniele Caprioli and Javier F Rubio and Leslie R Whitaker and Kylie B McPherson and Jennifer M Bossert and Yavin Shaham and Bruce T Hope},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27335401},
doi = {10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0140-16.2016},
issn = {1529-2401 (Electronic); 0270-6474 (Linking)},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-06-22},
journal = {J Neurosci},
volume = {36},
number = {25},
pages = {6691--6703},
address = {Behavioral Neuroscience Branch, Intramural Research Program/National Institute on Drug Abuse/National Institutes of Health/Department of Health and Human Services, Baltimore, Maryland 21224.},
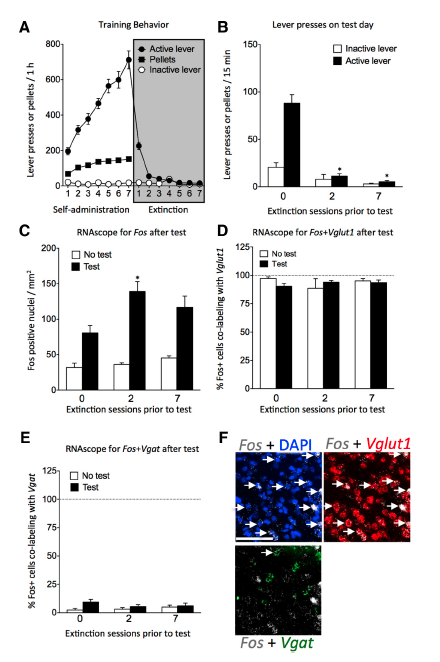
abstract = {UNLABELLED: In operant learning, initial reward-associated memories are thought to be distinct from subsequent extinction-associated memories. Memories formed during operant learning are thought to be stored in "neuronal ensembles." Thus, we hypothesize that different neuronal ensembles encode reward- and extinction-associated memories. Here, we examined prefrontal cortex neuronal ensembles involved in the recall of reward and extinction memories of food self-administration. We first trained rats to lever press for palatable food pellets for 7 d (1 h/d) and then exposed them to 0, 2, or 7 daily extinction sessions in which lever presses were not reinforced. Twenty-four hours after the last training or extinction session, we exposed the rats to either a short 15 min extinction test session or left them in their homecage (a control condition). We found maximal Fos (a neuronal activity marker) immunoreactivity in the ventral medial prefrontal cortex of rats that previously received 2 extinction sessions, suggesting that neuronal ensembles in this area encode extinction memories. We then used the Daun02 inactivation procedure to selectively disrupt ventral medial prefrontal cortex neuronal ensembles that were activated during the 15 min extinction session following 0 (no extinction) or 2 prior extinction sessions to determine the effects of inactivating the putative food reward and extinction ensembles, respectively, on subsequent nonreinforced food seeking 2 d later. Inactivation of the food reward ensembles decreased food seeking, whereas inactivation of the extinction ensembles increased food seeking. Our results indicate that distinct neuronal ensembles encoding operant reward and extinction memories intermingle within the same cortical area. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: A current popular hypothesis is that neuronal ensembles in different prefrontal cortex areas control reward-associated versus extinction-associated memories: the dorsal medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) promotes reward seeking, whereas the ventral mPFC inhibits reward seeking. In this paper, we use the Daun02 chemogenetic inactivation procedure to demonstrate that Fos-expressing neuronal ensembles mediating both food reward and extinction memories intermingle within the same ventral mPFC area.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
UNLABELLED: In operant learning, initial reward-associated memories are thought to be distinct from subsequent extinction-associated memories. Memories formed during operant learning are thought to be stored in "neuronal ensembles." Thus, we hypothesize that different neuronal ensembles encode reward- and extinction-associated memories. Here, we examined prefrontal cortex neuronal ensembles involved in the recall of reward and extinction memories of food self-administration. We first trained rats to lever press for palatable food pellets for 7 d (1 h/d) and then exposed them to 0, 2, or 7 daily extinction sessions in which lever presses were not reinforced. Twenty-four hours after the last training or extinction session, we exposed the rats to either a short 15 min extinction test session or left them in their homecage (a control condition). We found maximal Fos (a neuronal activity marker) immunoreactivity in the ventral medial prefrontal cortex of rats that previously received 2 extinction sessions, suggesting that neuronal ensembles in this area encode extinction memories. We then used the Daun02 inactivation procedure to selectively disrupt ventral medial prefrontal cortex neuronal ensembles that were activated during the 15 min extinction session following 0 (no extinction) or 2 prior extinction sessions to determine the effects of inactivating the putative food reward and extinction ensembles, respectively, on subsequent nonreinforced food seeking 2 d later. Inactivation of the food reward ensembles decreased food seeking, whereas inactivation of the extinction ensembles increased food seeking. Our results indicate that distinct neuronal ensembles encoding operant reward and extinction memories intermingle within the same cortical area. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: A current popular hypothesis is that neuronal ensembles in different prefrontal cortex areas control reward-associated versus extinction-associated memories: the dorsal medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) promotes reward seeking, whereas the ventral mPFC inhibits reward seeking. In this paper, we use the Daun02 chemogenetic inactivation procedure to demonstrate that Fos-expressing neuronal ensembles mediating both food reward and extinction memories intermingle within the same ventral mPFC area.