Featured Paper of the Month – August 2015
Root, David H; Hoffman, Alexander F; Good, Cameron H; Zhang, Shiliang; Gigante, Eduardo; Lupica, Carl R; Morales, Marisela
Norepinephrine activates dopamine D4 receptors in the rat lateral habenula. Journal Article
In: J Neurosci, vol. 35, no. 8, pp. 3460–3469, 2015, ISSN: 1529-2401 (Electronic); 0270-6474 (Linking).
@article{Root2015,
title = {Norepinephrine activates dopamine D4 receptors in the rat lateral habenula.},
author = {David H Root and Alexander F Hoffman and Cameron H Good and Shiliang Zhang and Eduardo Gigante and Carl R Lupica and Marisela Morales},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25716845},
doi = {10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4525-13.2015},
issn = {1529-2401 (Electronic); 0270-6474 (Linking)},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-02-25},
journal = {J Neurosci},
volume = {35},
number = {8},
pages = {3460--3469},
address = {Neuronal Networks Section, Integrative Neuroscience Research Branch and.},
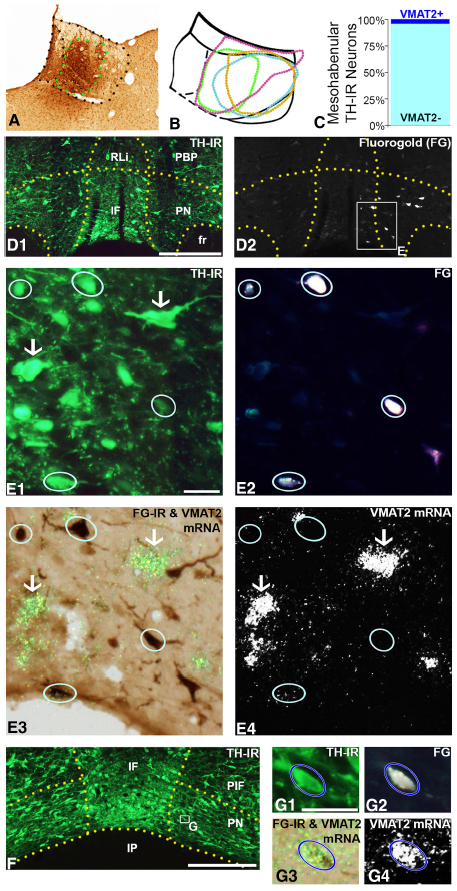
abstract = {The lateral habenula (LHb) is involved in reward and aversion and is reciprocally connected with dopamine (DA)-containing brain regions, including the ventral tegmental area (VTA). We used a multidisciplinary approach to examine the properties of DA afferents to the LHb in the rat. We find that >90% of VTA tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) neurons projecting to the LHb lack vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) mRNA, and there is little coexpression of TH and VMAT2 protein in this mesohabenular pathway. Consistent with this, electrical stimulation of LHb did not evoke DA-like signals, assessed with fast-scan cyclic voltammetry. However, electrophysiological currents that were inhibited by L741,742, a DA-D4-receptor antagonist, were observed in LHb neurons when DA uptake or degradation was blocked. To prevent DA activation of D4 receptors, we repeated this experiment in LHb slices from DA-depleted rats. However, this did not disrupt D4 receptor activation initiated by the dopamine transporter inhibitor, GBR12935. As the LHb is also targeted by noradrenergic afferents, we examined whether GBR12935 activation of DA-D4 receptors occurred in slices depleted of norepinephrine (NE). Unlike DA, NE depletion prevented the activation of DA-D4 receptors. Moreover, direct application of NE elicited currents in LHb neurons that were blocked by L741,742, and GBR12935 was found to be a more effective blocker of NE uptake than the NE-selective transport inhibitor nisoxetine. These findings demonstrate that NE is released in the rat LHb under basal conditions and that it activates DA-D4 receptors. Therefore, NE may be an important regulator of LHb function.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The lateral habenula (LHb) is involved in reward and aversion and is reciprocally connected with dopamine (DA)-containing brain regions, including the ventral tegmental area (VTA). We used a multidisciplinary approach to examine the properties of DA afferents to the LHb in the rat. We find that >90% of VTA tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) neurons projecting to the LHb lack vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) mRNA, and there is little coexpression of TH and VMAT2 protein in this mesohabenular pathway. Consistent with this, electrical stimulation of LHb did not evoke DA-like signals, assessed with fast-scan cyclic voltammetry. However, electrophysiological currents that were inhibited by L741,742, a DA-D4-receptor antagonist, were observed in LHb neurons when DA uptake or degradation was blocked. To prevent DA activation of D4 receptors, we repeated this experiment in LHb slices from DA-depleted rats. However, this did not disrupt D4 receptor activation initiated by the dopamine transporter inhibitor, GBR12935. As the LHb is also targeted by noradrenergic afferents, we examined whether GBR12935 activation of DA-D4 receptors occurred in slices depleted of norepinephrine (NE). Unlike DA, NE depletion prevented the activation of DA-D4 receptors. Moreover, direct application of NE elicited currents in LHb neurons that were blocked by L741,742, and GBR12935 was found to be a more effective blocker of NE uptake than the NE-selective transport inhibitor nisoxetine. These findings demonstrate that NE is released in the rat LHb under basal conditions and that it activates DA-D4 receptors. Therefore, NE may be an important regulator of LHb function.