Featured Paper of the Month – October 2023
Published in Drug and Alcohol Dependence with contributions from Michael Baumann and colleagues from the NIDA IRP.
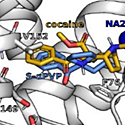
For this study, we examined the pharmacological effects of non-fentanyl synthetic opioids, including U-47700, brorphine, and isotonitazene, as compared to morphine and fentanyl.