Hot Off the Press – August 27 , 2020. This paper describes a new non-invasive model of opioid addiction in mice that is based on fentanyl vapor self-administration. This model allows the study of limited and prolonged drug intake, abstinence, and relapse to drug seeking. Compared to current intravenous models, the new model is more… [Read More]
Hot off the Press
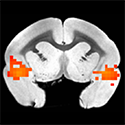
Converging structural and functional evidence for a rat salience network
Hot Off the Press – July 17 , 2020. The human salience network (SN) detects relevant stimuli to guide behavior and is implicated in neuropsychiatric diseases. In this study, we identified a functionally and structurally connected rat SN sharing spatial similarity with humans. We further demonstrated the functional implications of this network with conditioned heroin… [Read More]
New Challenges in Addiction Medicine: COVID-19 Infection in Patients With Alcohol and Substance Use Disorders-The Perfect Storm
Hot Off the Press – July 14 , 2020. In this article the authors discuss the heightened risks for individuals living with alcohol and substance use disorders during the current COVID-19 pandemic. Physiological, psychological, medical and economic consequences are described in relation to inaction including the far-reaching implications on the individual, society and global sphere…. [Read More]
Abstinence-dependent dissociable central amygdala microcircuits control drug craving
Hot Off the Press – March 27 , 2020. The current study offers a mechanistic explanation for the protective effect of social interaction on incubation of craving in rodents, showing that it is mediated by the activation of neurons expressing the enzyme PKCδ the brain’s amygdala. The study also shows that activation of a peptide… [Read More]
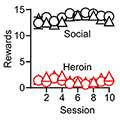
Operant Social Reward Decreases Incubation of Heroin Craving in Male and Female Rats.
Hot Off the Press – December 18 , 2019. We recently developed a rat model of relapse after voluntary abstinence from methamphetamine self-administration that is based on behavioral treatments in humans with substance use problems. In the present study, we extend this work to heroin self-administration, demonstrating that when rats are given the opportunity to… [Read More]
Habenular and striatal activity during performance feedback are differentially linked with state-like and trait-like aspects of tobacco use disorder.
Hot Off the Press – October 28, 2019. Approximately 1.1 billion people smoke cigarettes worldwide. More than half of these are expected to die of smoking-related diseases. According to the US Centers for Disease Control: most smokers (68%) want to quit; about half (54%) try to quit each year; yet very few (about 7%) do… [Read More]
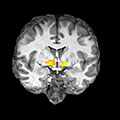
Altered corticolimbic control of the nucleus accumbens by chronic Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Exposure
Hot Off the Press – September 3, 2019. The expanding legalization of recreational and medical marijuana has increased its availability, and stronger strains of cannabis containing much higher levels of ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive constituent, are now widely used. Although the effects of marijuana on the brain are often assumed to be mild, there… [Read More]
High-Frequency Activation of Nucleus Accumbens D1-MSNs Drives Excitatory Potentiation on D2-MSNs.
Hot Off the Press – June 16, 2019. Brain stimulation is used to treat reward-related psychiatric diseases including addiction and treatment resistant depression. We report that high frequency stimulation parameters effective in treating these diseases promote the release of the peptide substance P. Release of this peptide in the Nucleus Accumbens rebalances excitatory input to… [Read More]
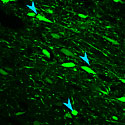
Neuron-Specific Genome Modification in the Adult Rat Brain Using CRISPR-Cas9 Transgenic Rats.
Hot Off the Press – May 10, 2019. Cell-specific CRISPR/Cas9 in the adult rat brain. Microscopic images of the midbrain of a transgenic rat that selectively expresses Cas9 in dopamine neurons. On the left side, control gRNAs were delivered to cells in the midbrain using a virus (green). On the right side, gRNAs to a… [Read More]
Compulsive drug use is associated with imbalance of orbitofrontal- and prelimbic-striatal circuits in punishment-resistant individuals
Hot Off the Press – May 6, 2019. We report that in a methamphetamine self-administration experiment, all rats show changes in the balance between “go” and “stop” brain circuits, however after foot shock punishment, behavior in the addictive subgroup is strongly correlated with the change in the balance of “go” and “stop” circuits, while the… [Read More]