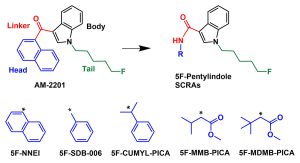
Chemical structures of 5F-pentylindole synthetic cannabinoids showing linker and head group variations, as compared to the parent compound AM-2201.
Featured Paper of the Month – May 2022
Published in Neuropsychopharmacology by Grant Glatfelter, John Partilla and Michael Baumann of the NIDA IRP Designer Drug Research Unit.
Summary
5F-MDMB-PICA is a potent synthetic cannabinoid associated with public harm from recreational use. Little is known about the pharmacology of 5F-MDMB-PICA underlying it’s potent effects. This study examined the pharmacological effects of 5F-MDMB-PICA at cannabinoid type 1 receptors (CB1) in mice relative to several structurally related compounds. Results show that certain structural features of the “head” groups of 5F-MDMB-PICA and related compounds dramatically impacts their potencies for CB1 mediated pharmacological effects and for producing cannabinoid-like effects in mice, which is predictive of potency of these compounds in humans.
Publication Information
Structure-activity relationships for 5F-MDMB-PICA and its 5F-pentylindole analogs to induce cannabinoid-like effects in mice Journal Article
In: Neuropsychopharmacology, vol. 47, no. 4, pp. 924–932, 2022, ISSN: 1740-634X.
