 Astrocytes modulate cerebral blood flow and neuronal response to cocaine in prefrontal cortex
Astrocytes modulate cerebral blood flow and neuronal response to cocaine in prefrontal cortex
Published in Mol Psychiatry.
Authors
Congwu Du, Kichon Park, Yueming Hua, Yanzuo Liu, Nora D Volkow, Yingtian Pan
Paper presented by Dr. Zilu Ma and selected by the NIDA TDI Paper of the Month Committee
Publication Brief Description
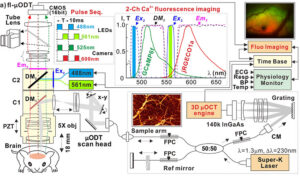
Cocaine disrupts multiple components of the neuro-glio-vascular (NGV) network in the brain, but distinguishing its effects on neurons, astrocytes, and blood vessels has remained a technical challenge due to their interactions. This study introduces a novel fl-ODM imaging system capable of capturing synchronized calcium activity in neurons and astrocytes alongside 3D cerebral blood flow velocity at high spatial and temporal resolution. Using this tool, this study demonstrates that astrocytes play a central role in mediating cocaine-induced vasoconstriction and modulating neuronal responses. Chemogenetic inhibition of astrocytic activity blunted both vascular and neuronal effects of cocaine, highlighting astrocytes as key regulators of neurovascular function and potential therapeutic targets. This technology provides a powerful platform for dissecting complex cellular interactions in vivo, with broad implications for studying brain function and pathology.
Astrocytes modulate cerebral blood flow and neuronal response to cocaine in prefrontal cortex Journal Article
In: Mol Psychiatry, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 820–834, 2024, ISSN: 1476-5578.
