Published in Nature (2021)
Authors
Kathryn Tunyasuvunakool, Jonas Adler, Zachary Wu, Tim Green, Michal Zielinski, Augustin Žídek, Alex Bridgland, Andrew Cowie, Clemens Meyer, Agata Laydon, Sameer Velankar, Gerard J. Kleywegt, Alex Bateman, Richard Evans, Alexander Pritzel, Michael Figurnov, Olaf Ronneberger, Russ Bates, Simon A. A. Kohl, Anna Potapenko, Andrew J. Ballard, Bernardino Romera-Paredes, Stanislav Nikolov, Rishub Jain, Ellen Clancy, David Reiman, Stig Petersen, Andrew W. Senior, Koray Kavukcuoglu, Ewan Birney, Pushmeet Kohli, John Jumper & Demis Hassabis
Paper presented by Dr. Joshua Hinkle and selected by the NIDA TDI Paper of the Month Committee
Publication Brief Description
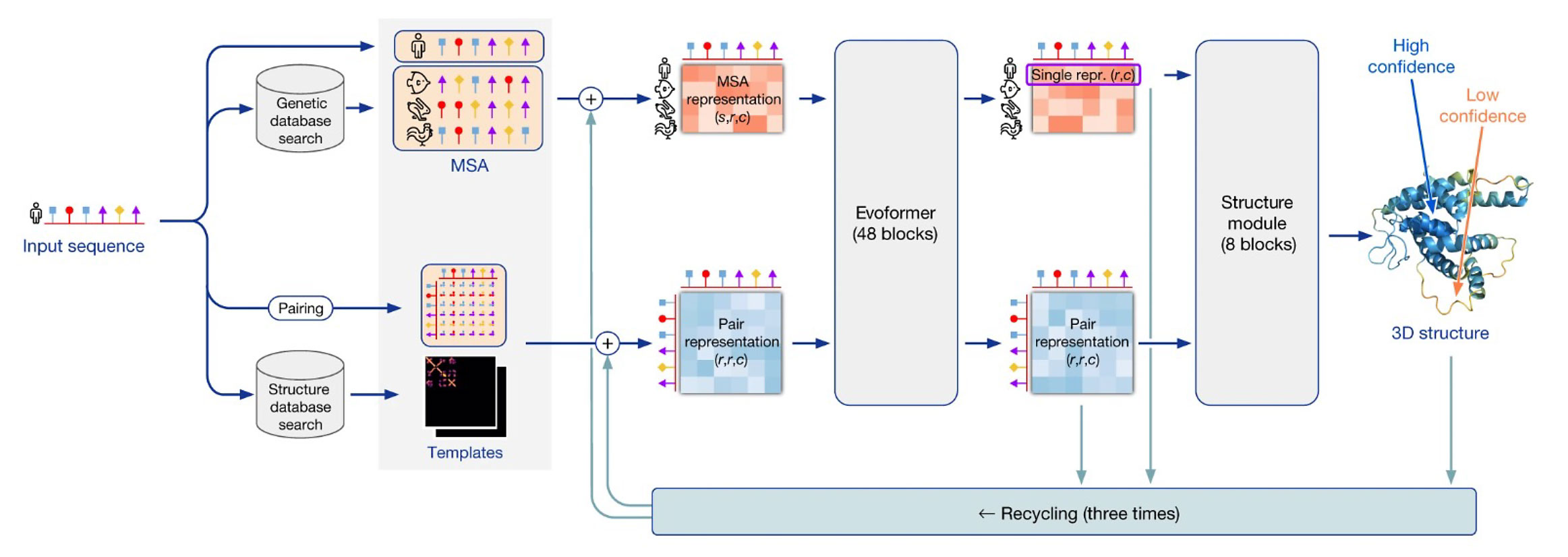
Determining complete protein structures is difficult as sufficient quantities need to be purified; protein size, transmembrane domains, and susceptibility to conformational changes create inconsistencies; and the work can take months to years. While protein sequence prediction is not new, increases in computation and artificial intelligence have enhanced accuracy and scale allowing for AlphaFold’s 3D machine learning to predict protein structure more accurately from primary sequence. Tunyasuvunakool et al. applied AlphaFold to predict full-length structures with detailed chemical components of nearly the entire human proteome (98.5%) as well as ~20 other organisms and provided this data in a public database. Since publication, the authors updated AlphaFold (version 2) shortening days-long prediction computation to minutes/hours and the database now has over 200 million protein structures. As current methods are used in conjunction with AlphaFold to validate predicted structures and improve machine learning, structure prediction accuracy will increase allowing for structures of proteins to be predicted in different molecular and cellular environments. The AlphaFold database is an invaluable resource for providing new insight into protein interactions, functions, and therapeutic drug development.
Highly accurate protein structure prediction for the human proteome Journal Article
In: Nature, vol. 596, no. 7873, pp. 590–596, 2021, ISSN: 1476-4687.