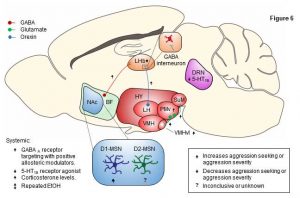
Inappropriate and pathological aggression plays a leading role in the suffering and death of millions of people, and further places an untenable strain on the caregivers and families of those afflicted. In some cases, like addictive drugs, aggression can be highly rewarding (appetitive) and continually pursued despite short- and long-term negative consequences. Similarly, recidivism (relapse) rates for violent offenders are as high as relapse rates for drug addicts. In this review, we first discuss the behavioral procedures developed to probe appetitive aggression in mice models and also describe the recently proposed phenomenon of “aggression addiction.” Next, we discuss the pharmacological and circuit mechanisms of aggression and aggression seeking (relapse), highlighting mechanistic congruence and divergence between appetitive and consummatory aggression.
For a related study, see:
Nucleus Accumbens Drd1-Expressing Neurons Control Aggression Self-Administration and Aggression Seeking in Mice
Animal Models of (or for) Aggression Reward, Addiction, and Relapse: Behavior and Circuits. Journal Article
In: J Neurosci, vol. 39, no. 21, pp. 3996–4008, 2019, ISSN: 1529-2401 (Electronic); 0270-6474 (Linking).