Hot Off the Press! – September 2014
McDevitt, Ross A; Tiran-Cappello, Alix; Shen, Hui; Balderas, Israela; Britt, Jonathan P; Marino, Rosa A M; Chung, Stephanie L; Richie, Christopher T; Harvey, Brandon K; Bonci, Antonello
Serotonergic versus Nonserotonergic Dorsal Raphe Projection Neurons: Differential Participation in Reward Circuitry Journal Article
In: Cell Reports, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 1857–1869, 2014, ISBN: 2211-1247.
@article{McDevitt2014,
title = {Serotonergic versus Nonserotonergic Dorsal Raphe Projection Neurons: Differential Participation in Reward Circuitry},
author = {Ross A McDevitt and Alix Tiran-Cappello and Hui Shen and Israela Balderas and Jonathan P Britt and Rosa A M Marino and Stephanie L Chung and Christopher T Richie and Brandon K Harvey and Antonello Bonci},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.037
http://www.cell.com/cell-reports/abstract/S2211-1247(14)00713-X},
doi = {10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.037},
isbn = {2211-1247},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-09-18},
booktitle = {Cell Reports},
journal = {Cell Reports},
volume = {8},
number = {6},
pages = {1857--1869},
publisher = {Elsevier},
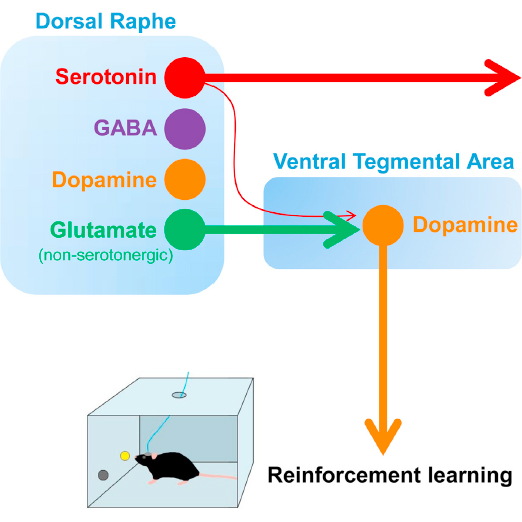
abstract = {The dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) contains the largest group of serotonin-producing neurons in the brain and projects to regions controlling reward. Although pharmacological studies suggest that serotonin inhibits reward seeking, electrical stimulation of the DRN strongly reinforces instrumental behavior. Here, we provide a targeted assessment of the behavioral, anatomical, and electrophysiological contributions of serotonergic and nonserotonergic DRN neurons to reward processes. To explore DRN heterogeneity, we used a simultaneous two-vector knockout/optogenetic stimulation strategy, as well as cre-induced and cre-silenced vectors in several cre-expressing transgenic mouse lines. We found that the DRN is capable of reinforcing behavior primarily via nonserotonergic neurons, for which the main projection target is the ventral tegmental area (VTA). Furthermore, these nonserotonergic projections provide glutamatergic excitation of VTA dopamine neurons and account for a large majority of the DRN-VTA pathway. These findings help to resolve apparent discrepancies between the roles of serotonin versus the DRN in behavioral reinforcement.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) contains the largest group of serotonin-producing neurons in the brain and projects to regions controlling reward. Although pharmacological studies suggest that serotonin inhibits reward seeking, electrical stimulation of the DRN strongly reinforces instrumental behavior. Here, we provide a targeted assessment of the behavioral, anatomical, and electrophysiological contributions of serotonergic and nonserotonergic DRN neurons to reward processes. To explore DRN heterogeneity, we used a simultaneous two-vector knockout/optogenetic stimulation strategy, as well as cre-induced and cre-silenced vectors in several cre-expressing transgenic mouse lines. We found that the DRN is capable of reinforcing behavior primarily via nonserotonergic neurons, for which the main projection target is the ventral tegmental area (VTA). Furthermore, these nonserotonergic projections provide glutamatergic excitation of VTA dopamine neurons and account for a large majority of the DRN-VTA pathway. These findings help to resolve apparent discrepancies between the roles of serotonin versus the DRN in behavioral reinforcement.