Hot Off the Press – November 11 , 2020
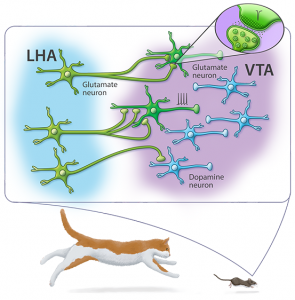
The role of ventral tegmental area (VTA) in motivated behavior is well established. However, Barbano et al., demonstrated that a subset of VTA neurons, that utilizes glutamate as signaling molecule, mediates innate defensive behaviors, evolutionary selected responses that promote escaping from dangerous situations. Alterations in innate defensive behavior have been associated with psychiatric disorders, such as PTSD and autism. The unanticipated role of VTA glutamate neurons in mediating innate defense opens new avenues to determine their role in brain disorders associated with the dysregulation of innate defensive behaviors in general, and dysregulation associated with intake of drugs of abuse in particular.
Publication Information
VTA Glutamatergic Neurons Mediate Innate Defensive Behaviors Journal Article
In: Neuron, vol. 107, no. 2, pp. 368–382.e8, 2020, ISBN: 0896-6273.