Hot Off the Press! – November 2014
Qi, Jia; Zhang, Shiliang; Wang, Hui-Ling; Wang, Huikun; de Jesus Aceves Buendia, Jose; Hoffman, Alexander F; Lupica, Carl R; Seal, Rebecca P; Morales, Marisela
A glutamatergic reward input from the dorsal raphe to ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. Journal Article
In: Nat Commun, vol. 5, pp. 5390, 2014, ISSN: 2041-1723 (Electronic); 2041-1723 (Linking).
@article{Qi2014,
title = {A glutamatergic reward input from the dorsal raphe to ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons.},
author = {Jia Qi and Shiliang Zhang and Hui-Ling Wang and Huikun Wang and Jose de Jesus Aceves Buendia and Alexander F Hoffman and Carl R Lupica and Rebecca P Seal and Marisela Morales},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25388237},
doi = {10.1038/ncomms6390},
issn = {2041-1723 (Electronic); 2041-1723 (Linking)},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-11-12},
journal = {Nat Commun},
volume = {5},
pages = {5390},
address = {National Institute on Drug Abuse, Neuronal Networks Section, National Institutes of Health, Baltimore, Maryland, USA.},
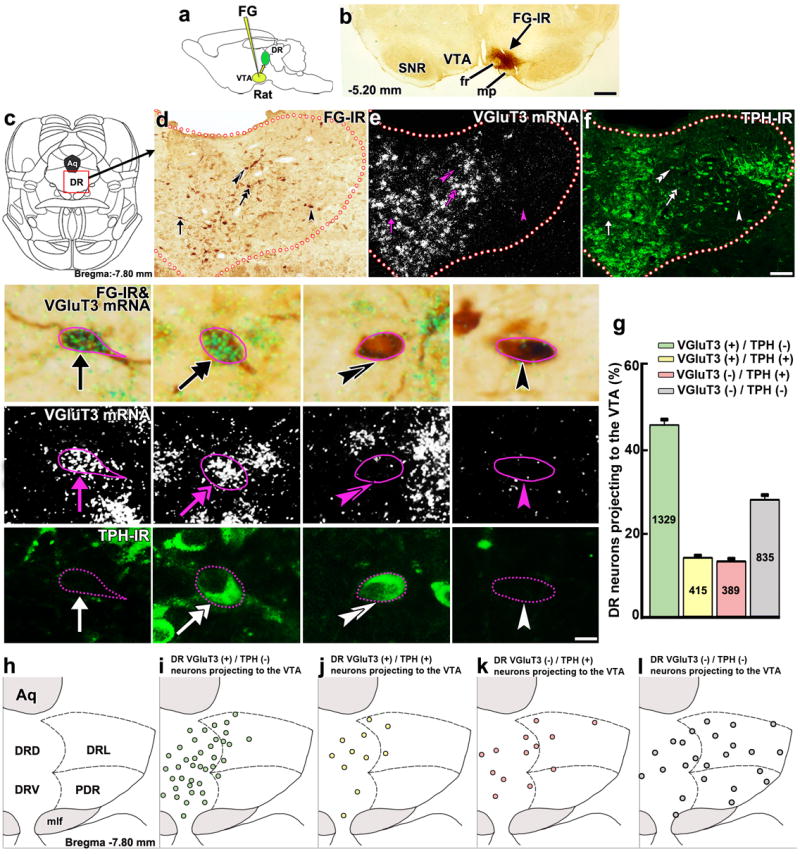
abstract = {Electrical stimulation of the dorsal raphe (DR) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) activates the fibres of the same reward pathway but the phenotype of this pathway and the direction of the reward-relevant fibres have not been determined. Here we report rewarding effects following activation of a DR-originating pathway consisting of vesicular glutamate transporter 3 (VGluT3) containing neurons that form asymmetric synapses onto VTA dopamine neurons that project to nucleus accumbens. Optogenetic VTA activation of this projection elicits AMPA-mediated synaptic excitatory currents in VTA mesoaccumbens dopaminergic neurons and causes dopamine release in nucleus accumbens. Activation also reinforces instrumental behaviour and establishes conditioned place preferences. These findings indicate that the DR-VGluT3 pathway to VTA utilizes glutamate as a neurotransmitter and is a substrate linking the DR-one of the most sensitive reward sites in the brain--to VTA dopaminergic neurons.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Electrical stimulation of the dorsal raphe (DR) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) activates the fibres of the same reward pathway but the phenotype of this pathway and the direction of the reward-relevant fibres have not been determined. Here we report rewarding effects following activation of a DR-originating pathway consisting of vesicular glutamate transporter 3 (VGluT3) containing neurons that form asymmetric synapses onto VTA dopamine neurons that project to nucleus accumbens. Optogenetic VTA activation of this projection elicits AMPA-mediated synaptic excitatory currents in VTA mesoaccumbens dopaminergic neurons and causes dopamine release in nucleus accumbens. Activation also reinforces instrumental behaviour and establishes conditioned place preferences. These findings indicate that the DR-VGluT3 pathway to VTA utilizes glutamate as a neurotransmitter and is a substrate linking the DR-one of the most sensitive reward sites in the brain--to VTA dopaminergic neurons.