Hot Off the Press! – March 2016
Qi, Jia; Zhang, Shiliang; Wang, Hui-Ling; Barker, David J; Miranda-Barrientos, Jorge; Morales, Marisela
VTA glutamatergic inputs to nucleus accumbens drive aversion by acting on GABAergic interneurons. Journal Article
In: Nat Neurosci, vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 725–733, 2016, ISSN: 1546-1726 (Electronic); 1097-6256 (Linking).
@article{Qi2016,
title = {VTA glutamatergic inputs to nucleus accumbens drive aversion by acting on GABAergic interneurons.},
author = {Jia Qi and Shiliang Zhang and Hui-Ling Wang and David J Barker and Jorge Miranda-Barrientos and Marisela Morales},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27019014},
doi = {10.1038/nn.4281},
issn = {1546-1726 (Electronic); 1097-6256 (Linking)},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-05-01},
journal = {Nat Neurosci},
volume = {19},
number = {5},
pages = {725--733},
address = {Neuronal Networks Section, Integrative Neuroscience Research Branch, US National Institute on Drug Abuse, Baltimore, Maryland, USA.},
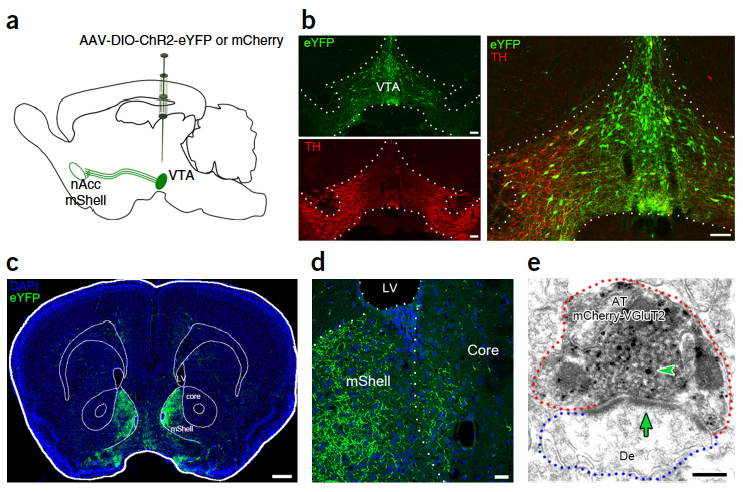
abstract = {The ventral tegmental area (VTA) is best known for its dopamine neurons, some of which project to nucleus accumbens (nAcc). However, the VTA also has glutamatergic neurons that project to nAcc. The function of the mesoaccumbens glutamatergic pathway remains unknown. Here we report that nAcc photoactivation of mesoaccumbens glutamatergic fibers promotes aversion. Although we found that these mesoaccumbens glutamatergic fibers lack GABA, the aversion evoked by their photoactivation depended on glutamate- and GABA-receptor signaling, and not on dopamine-receptor signaling. We found that mesoaccumbens glutamatergic fibers established multiple asymmetric synapses on single parvalbumin GABAergic interneurons and that nAcc photoactivation of these fibers drove AMPA-mediated cellular firing of parvalbumin GABAergic interneurons. These parvalbumin GABAergic interneurons in turn inhibited nAcc medium spiny output neurons, thereby controlling inhibitory neurotransmission in nAcc. To our knowledge, the mesoaccumbens glutamatergic pathway is the first glutamatergic input to nAcc shown to mediate aversion instead of reward, and the first pathway shown to establish excitatory synapses on nAcc parvalbumin GABAergic interneurons.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) is best known for its dopamine neurons, some of which project to nucleus accumbens (nAcc). However, the VTA also has glutamatergic neurons that project to nAcc. The function of the mesoaccumbens glutamatergic pathway remains unknown. Here we report that nAcc photoactivation of mesoaccumbens glutamatergic fibers promotes aversion. Although we found that these mesoaccumbens glutamatergic fibers lack GABA, the aversion evoked by their photoactivation depended on glutamate- and GABA-receptor signaling, and not on dopamine-receptor signaling. We found that mesoaccumbens glutamatergic fibers established multiple asymmetric synapses on single parvalbumin GABAergic interneurons and that nAcc photoactivation of these fibers drove AMPA-mediated cellular firing of parvalbumin GABAergic interneurons. These parvalbumin GABAergic interneurons in turn inhibited nAcc medium spiny output neurons, thereby controlling inhibitory neurotransmission in nAcc. To our knowledge, the mesoaccumbens glutamatergic pathway is the first glutamatergic input to nAcc shown to mediate aversion instead of reward, and the first pathway shown to establish excitatory synapses on nAcc parvalbumin GABAergic interneurons.