Hot Off the Press! – January 2017
Tejeda, Hugo A; Wu, Jocelyn; Kornspun, Alana R; Pignatelli, Marco; Kashtelyan, Vadim; Krashes, Michael J; Lowell, Brad B; Carlezon, William A Jr; Bonci, Antonello
In: Neuron, vol. 93, no. 1, pp. 147-163, 2017, ISSN: 1097-4199 (Electronic); 0896-6273 (Linking).
@article{Tejeda2017,
title = {Pathway- and Cell-Specific Kappa-Opioid Receptor Modulation of Excitation-Inhibition Balance Differentially Gates D1 and D2 Accumbens Neuron Activity.},
author = {Tejeda, Hugo A and Wu, Jocelyn and Kornspun, Alana R and Pignatelli, Marco and Kashtelyan, Vadim and Krashes, Michael J and Lowell, Brad B and Carlezon, William A Jr and Bonci, Antonello},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28056342},
doi = {10.1016/j.neuron.2016.12.005},
issn = {1097-4199 (Electronic); 0896-6273 (Linking)},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-01-04},
journal = {Neuron},
volume = {93},
number = {1},
pages = {147-163},
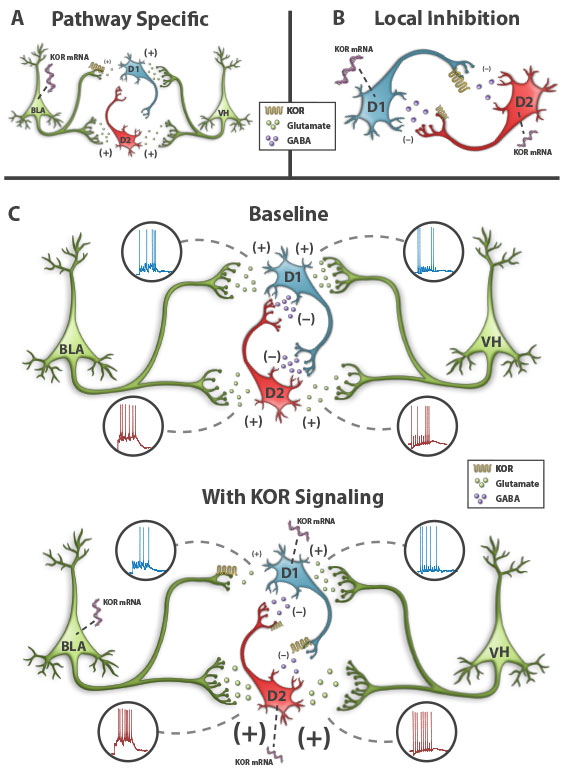
abstract = {Endogenous dynorphin signaling via the kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) in the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) powerfully mediates negative affective states and stress reactivity. Excitatory inputs from the hippocampus and amygdala play a fundamental role in shaping the activity of both NAcc D1 and D2 MSNs, which encode positive and negative motivational valences, respectively. However, a circuit-based mechanism by which KOR modulation of excitation-inhibition balance modifies D1 and D2 MSN activity is lacking. Here, we provide a comprehensive synaptic framework wherein presynaptic KOR inhibition decreases the excitatory drive of D1 MSN activity by the amygdala, but not the hippocampus. Conversely, presynaptic inhibition by KORs of inhibitory synapses on D2 MSNs enhances integration of excitatory drive by the amygdala and hippocampus. In conclusion, we describe a circuit-based mechanism showing differential gating of afferent control of D1 and D2 MSN activity by KORs in a pathway-specific manner.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Endogenous dynorphin signaling via the kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) in the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) powerfully mediates negative affective states and stress reactivity. Excitatory inputs from the hippocampus and amygdala play a fundamental role in shaping the activity of both NAcc D1 and D2 MSNs, which encode positive and negative motivational valences, respectively. However, a circuit-based mechanism by which KOR modulation of excitation-inhibition balance modifies D1 and D2 MSN activity is lacking. Here, we provide a comprehensive synaptic framework wherein presynaptic KOR inhibition decreases the excitatory drive of D1 MSN activity by the amygdala, but not the hippocampus. Conversely, presynaptic inhibition by KORs of inhibitory synapses on D2 MSNs enhances integration of excitatory drive by the amygdala and hippocampus. In conclusion, we describe a circuit-based mechanism showing differential gating of afferent control of D1 and D2 MSN activity by KORs in a pathway-specific manner.