Hot Off the Press – April 12, 2019.
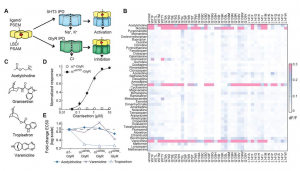
NIDA-funded scientists have just published findings in the journal Science showing the development of a new, groundbreaking chemogenetics technology for modulating brain function in a remote, precise and ultra-sensitive manner in living subjects. These findings describe new chemogenetic ion channels for neuron activation and silencing that are controlled by very low doses of the anti-smoking medication varenicline. This drug is an especially attractive molecule for chemogenetic applications in part because it is well-tolerated by patients, effectively penetrates the brain, and has long-lasting effects. This technique for modulating neuronal function, reported in laboratory animals, has potential for use in humans, and may pave the way for new treatments for addiction, pain, depression, and other conditions. Ongoing experiments at NIDA are already applying this technology to study malfunctioning brain circuits and their relevance to development of drug addiction.
The work was funded by NIDA; participating scientists were from NIDA’s Intramural Research program in Baltimore, Janelia: Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Janelia Research Campus, New York University, Emory University and the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine
Publication Information
Ultrapotent chemogenetics for research and potential clinical applications. Journal Article
In: Science, 2019, ISSN: 1095-9203 (Electronic); 0036-8075 (Linking).