 Featured Paper of the Month – January 2021
Featured Paper of the Month – January 2021
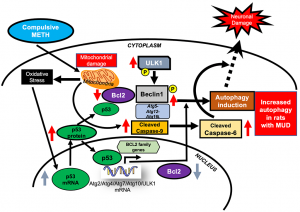
The use of methamphetamine (METH) is very prevalent throughout the world. METH can cause anxiety, psychosis, seizures, and death. Previous research in the Cadet Lab has shown that METH can cause neurodegeneration when the drug is injected by investigators. It was therefore important to find out if there is degeneration in the brains of rats that learn to give themselves METH by a behavioral technique called self-administration (SA). In that model, rats are trained to self-administer METH and then get footshocks as punishment to see if they will stop or continue to take the drug. In general, 40% of rats will continue to take METH compulsively even in the presence of the shocks. We found that animals that continue to take METH have changes in the brain expression of some genes, namely Atg5, Atg14, and Atg16L1, that are related to a process called autophagy. Abnormalities in autophagy have been reported in some neurological diseases. The brains of the compulsive METH takers also show increases in the levels of some proteins involved in regulating autophagy. Moreover, these compulsive METH takers showed increased expression of proteins involved in causing cell death but decreased in a protein called Bcl-2 that protects against cell death. These results tell us that compulsive METH taking can result in pathological changes similar to what is reported when investigators give the drug to rats. These observations also tell us that we need to develop treatments that can help the brains of users who take too much METH.
Publication Information
Compulsive methamphetamine taking induces autophagic and apoptotic markers in the rat dorsal striatum Journal Article
In: Archives of Toxicology, vol. 94, no. 10, pp. 3515–3526, 2020, ISBN: 1432-0738.
