Featured Paper of the Month – October 2015
Stolzenberg, S.; Quick, M.; Zhao, C.; Gotfryd, K.; Khelashvili, G.; Gether, U.; Loland, C. J.; Javitch, J. A.; Noskov, S.; Weinstein, H.; Shi, L.
Mechanism of the Association between Na+ Binding and Conformations at the Intracellular Gate in Neurotransmitter:Sodium Symporters. Journal Article
In: J Biol Chem, vol. 290, no. 22, pp. 13992–14003, 2015, ISSN: 1083-351X (Electronic); 0021-9258 (Linking).
@article{Stolzenberg2015,
title = {Mechanism of the Association between Na+ Binding and Conformations at the Intracellular Gate in Neurotransmitter:Sodium Symporters.},
author = {Stolzenberg, S. and Quick, M. and Zhao, C. and Gotfryd, K. and Khelashvili, G. and Gether, U. and Loland, C. J. and Javitch, J. A. and Noskov, S. and Weinstein, H. and Shi, L.},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25869126},
doi = {10.1074/jbc.M114.625343},
issn = {1083-351X (Electronic); 0021-9258 (Linking)},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-05-29},
urldate = {2015-05-29},
journal = {J Biol Chem},
volume = {290},
number = {22},
pages = {13992--14003},
address = {From the Department of Physiology and Biophysics and the Department of Physics, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, 14850.},
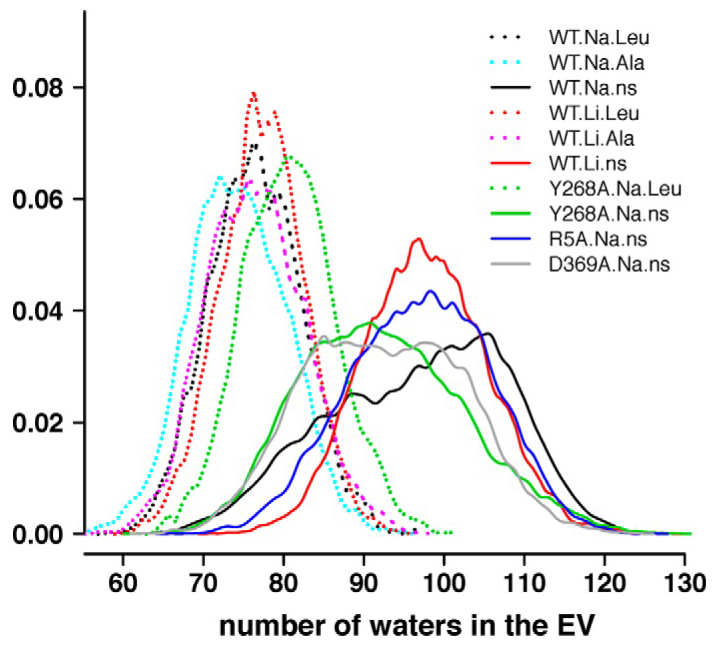
abstract = {Neurotransmitter:sodium symporters (NSSs) terminate neurotransmission by Na(+)-dependent reuptake of released neurotransmitters. Previous studies suggested that Na(+)-binding reconfigures dynamically coupled structural elements in an allosteric interaction network (AIN) responsible for function-related conformational changes, but the intramolecular pathway of this mechanism has remained uncharted. We describe a new approach for the modeling and analysis of intramolecular dynamics in the bacterial NSS homolog LeuT. From microsecond-scale molecular dynamics simulations and cognate experimental verifications in both LeuT and human dopamine transporter (hDAT), we apply the novel method to identify the composition and the dynamic properties of their conserved AIN. In LeuT, two different perturbations disrupting Na(+) binding and transport (i.e. replacing Na(+) with Li(+) or the Y268A mutation at the intracellular gate) affect the AIN in strikingly similar ways. In contrast, other mutations that affect the intracellular gate (i.e. R5A and D369A) do not significantly impair Na(+) cooperativity and transport. Our analysis shows these perturbations to have much lesser effects on the AIN, underscoring the sensitivity of this novel method to the mechanistic nature of the perturbation. Notably, this set of observations holds as well for hDAT, where the aligned Y335A, R60A, and D436A mutations also produce different impacts on Na(+) dependence. Thus, the detailed AIN generated from our method is shown to connect Na(+) binding with global conformational changes that are critical for the transport mechanism. That the AIN between the Na(+) binding sites and the intracellular gate in bacterial LeuT resembles that in eukaryotic hDAT highlights the conservation of allosteric pathways underlying NSS function.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Neurotransmitter:sodium symporters (NSSs) terminate neurotransmission by Na(+)-dependent reuptake of released neurotransmitters. Previous studies suggested that Na(+)-binding reconfigures dynamically coupled structural elements in an allosteric interaction network (AIN) responsible for function-related conformational changes, but the intramolecular pathway of this mechanism has remained uncharted. We describe a new approach for the modeling and analysis of intramolecular dynamics in the bacterial NSS homolog LeuT. From microsecond-scale molecular dynamics simulations and cognate experimental verifications in both LeuT and human dopamine transporter (hDAT), we apply the novel method to identify the composition and the dynamic properties of their conserved AIN. In LeuT, two different perturbations disrupting Na(+) binding and transport (i.e. replacing Na(+) with Li(+) or the Y268A mutation at the intracellular gate) affect the AIN in strikingly similar ways. In contrast, other mutations that affect the intracellular gate (i.e. R5A and D369A) do not significantly impair Na(+) cooperativity and transport. Our analysis shows these perturbations to have much lesser effects on the AIN, underscoring the sensitivity of this novel method to the mechanistic nature of the perturbation. Notably, this set of observations holds as well for hDAT, where the aligned Y335A, R60A, and D436A mutations also produce different impacts on Na(+) dependence. Thus, the detailed AIN generated from our method is shown to connect Na(+) binding with global conformational changes that are critical for the transport mechanism. That the AIN between the Na(+) binding sites and the intracellular gate in bacterial LeuT resembles that in eukaryotic hDAT highlights the conservation of allosteric pathways underlying NSS function.