 Featured Paper of the Month – May 2019.
Featured Paper of the Month – May 2019.
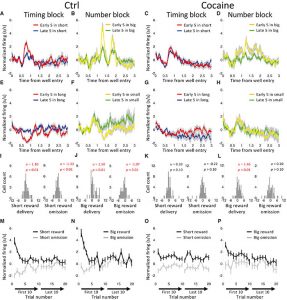
Addiction is a disorder of behavioral control and learning. While this may reflect pre-existing propensities, drug use also clearly contributes by causing changes in outcome processing in prefrontal and striatal regions. This altered processing is associated with behavioral deficits, including changes in learning. These areas provide critical input to midbrain dopamine neurons regarding expected outcomes, suggesting that effects on learning may result from changes in dopaminergic error signaling. Here, we show that dopamine neurons recorded in rats that had self-administered cocaine failed to suppress firing on omission of an expected reward and exhibited lower amplitude and imprecisely timed increases in firing to an unexpected reward. Learning also appeared to have less of an effect on reward-evoked and cue-evoked firing in the cocaine-experienced rats. Overall, the changes are consistent with reduced fidelity of input regarding the expected outcomes, such as their size, timing, and overall value, because of cocaine use.
Publication Information
Expectancy-Related Changes in Dopaminergic Error Signals Are Impaired by Cocaine Self-Administration. Journal Article
In: Neuron, vol. 101, no. 2, pp. 294–306, 2019, ISSN: 1097-4199 (Electronic); 0896-6273 (Linking).
