Featured Paper of the Month – March 2019.
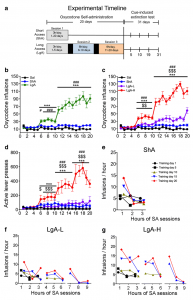
Abuse of opioids including oxycodone is very prevalent in the US. Researchers in the laboratory of Jean Lud Cadet in the NIDA IRP have shown that when rats are given access to oxycodone for several hours, some of the rats will increase the amount of the drug in a very steep fashion whereas others will only take moderate quantities of the drug. They also found, however, that, after a month of withdrawal from oxycodone, all those rats had decreased levels of mu opioid receptor protein in the dorsal striatum, a brain region that is important for habit forming. Decreases in striatal opioid receptor protein expression in these rats may be one of the reasons why addicted patients relapse to opioid seeking.
Publication Information
In: Mol Neurobiol, 2018, ISSN: 1559-1182 (Electronic); 0893-7648 (Linking).