Featured Paper of the Month – December 2017.
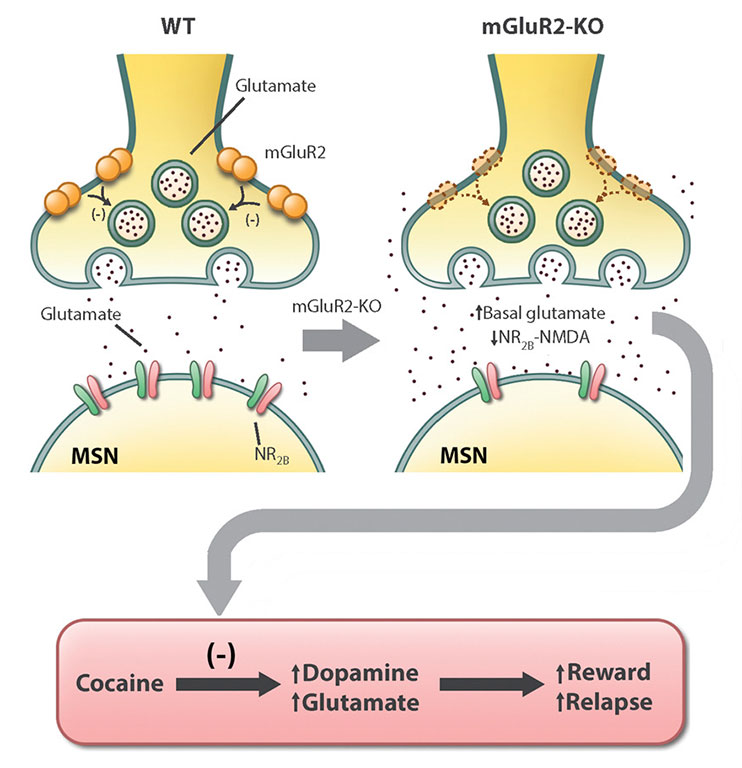
The etiology and pathophysiology of drug addiction are still not well understood. In this research paper, we show that genetic deletion of mGluR2, a presynaptic glutamate autoreceptor, decreases sensitivity to cocaine reward that causes a compensatory increase in cocaine intake and a decrease in relapse to cocaine-seeking behavior in rats.
Publication Information
Deletion of Type 2 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Decreases Sensitivity to Cocaine Reward in Rats. Journal Article
In: Cell Rep, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 319–332, 2017, ISSN: 2211-1247 (Electronic).