 Featured Paper of the Month – January 2020.
Featured Paper of the Month – January 2020.
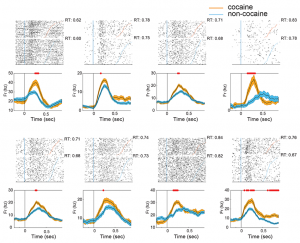
Drug-associated cues can intrude upon thinking, making relapse more likely. A measure of how strongly cues engage cognitive resources is called attentional bias. This is reflected in slightly longer response times on trials on a stimulus response task when drug cues are present compared to non-drug cues. In both cases, the cue is an irrelevant distractor that should just be ignored. Attentional bias is clinically important, because, across individuals, it correlates with extent of current use, and risk of relapse among those attempting abstinence. The lack of animal models of attentional bias has made it difficult to determine which brain regions are engaged by drug cues to produce attentional bias. We have developed such a model using cocaine-associated cues while simultaneously recording electrical activity in cortical and sub-cortical brain regions. As in clinical studies, attentional bias was indicated by elongated response times on trials with cocaine-associated distractors compared to trials with non-cocaine distractors. An area known to be involved in reward processing, the orbitofrontal cortex, was more activated by drug cues, both by neuronal population response, and the proportion of single neurons activated. Dorsal and ventral striatum, two areas also involved in reward processing, did not distinguish between drug and non-drug cues. These direct measures of single unit activity in an animal model complement clinical imaging observations suggesting that cortical mechanisms, especially in orbitofrontal cortex, are likely involved in attentional bias to cocaine associated environmental cues.
Publication Information
Orbitofrontal cortex is selectively activated in a primate model of attentional bias to cocaine cues. Journal Article
In: Neuropsychopharmacology, 2019, ISSN: 1740-634X (Electronic); 0893-133X (Linking).
